Data Communication and Networking Notes – OSI, TCP/IP Model
Data Communication is the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as wire cable.Communication can be defined as the exchange of information between one group or person and another group or person. This communication can be between people within the same organisation(internal communication) or with people or groups outside the organization(external communication).

The effectiveness of data communication system depends on four fundamental characteristics such as Delivery, accuracy, timeliness, and jitter.
- Delivery : The system must deliver data to the correct destination. Data must be recovered by user and only by the device.
- Accuracy : The system must deliver the data accurately.
- Timeliness : The system must deliver data in a timely manner. Data delivered late are useless.
- Jitter : Jitter refers to the variation in the packet arrival time.
In Data communication there are 4 basic terms-
- Data : Data are entities that convey meaning. Data are representation whereas information refer to the content or interpretation of data.
- Signal: Signals are electric or electromagnetic encoding of data.
- Signalling: Signalling is propagation of signal along suitable communication medium.
- Transmission: Transmission is communication of data by the proposition and processing of signals.
Components : A data communication system has five components.
- Message: The message is the information to be communicated , Information include text, number,pictures audio and video.
- Sender: The sender is the device that sends the data message. It can be a computer, worstation, telephone, video camera etc.
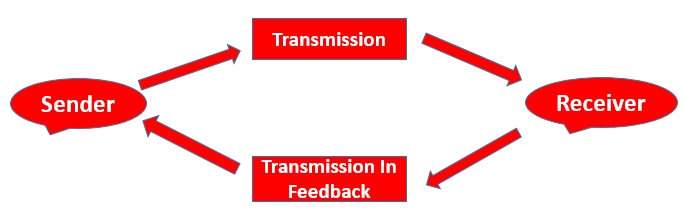
- Receiver : The receiver is the device that receive the message. It can bea computer, workstation, telephone, video camera etc.
- Transmission medium : Transmission medium is the physical path by which a message travels from sender and to receive . examples are twisted pair cable.
- Protocol : A protocol is a set of rules ( written in the form of program ) to perform specific task or action Eg. HTTP, FTP etc. that govern data communication . It represents a agreement between the communicating devices
Concept of Data Communication : The concept of Data Communication evolved from sharing the computation power of a computer along with various resources available in a computer environment such as printer , hard disk etc. Data Communication can be used to transfer as exchange confirmation within on building one city, across cities countries and continents.
Data Communication Code (Data encoding ): Every character (Letter, Number, symbol) is composed of a group of bits called Codes. The most widely used codes are the ASCII (American Standard code for Information Interchange), EBCDIC ( Extended Binary Coded decimal Interchange Code),
| Char | 7 bit ASCII | Hex |
| A | 100 0001 | 41 |
| B | 100 0010 | 42 |
| C | 100 0011 | 43 |
| D | 100 0100 | 44 |
| E | 100 0101 | 45 |
| F | 100 0110 | 46 |
| G | 100 0111 | 47 |
| H | 100 1000 | 48 |
| I | 100 1001 | 49 |
| J | 100 1010 | 4A |
| K | 100 1011 | 4B |
| L | 100 1100 | 4C |
| M | 100 1101 | 4D |
| N | 100 1110 | 4E |
| O | 100 1111 | 4F |
| P | 101 0000 | 50 |
| Q | 101 0001 | 51 |
| R | 101 0010 | 52 |
| S | 101 0011 | 53 |
| T | 101 0100 | 54 |
| U | 101 0101 | 55 |
| V | 101 0110 | 56 |
| W | 101 0111 | 57 |
| X | 101 1000 | 58 |
| Y | 101 1001 | 59 |
| Z | 101 1010 | 5A |
| a | 110 0001 | 61 |
| b | 110 0010 | 62 |
|
So on…
|
||
ASCII and Hex Codes of Characters
Communication Protocol/ Standard : Protocol is a set of rules that perform specific task. In other words, protocols are technical customs or guide -lines that govern the exchange of signal transmission and reception between equipments. Both hardware and software are designed to handle specific protocols.
Communication Speed or Rate : The speed at which two computers exchange or transmit data is called communication rate on transmission speed. The unit of measurement of the speed is measured in bits per second (bps) or band. Normal PC based communication transferred using 300 to Mbps whereas mainframe computers uses 19,200 baud.
Communication protocols are usually defined and approved by some International body such as ISO, CCITT or IEEE. Some of function on protocols regulates are :
- Control and Information transfer
- Structure and formats of data
- Error recoveries
- Retransmission
- Interface management
Protocol Layers :
The OSI (Open System Interconnection ) Data Model : It is ISO standard for computer networks design and functioning. It has 7 Layers and each layer playing a specific role when applications are communicating over the net.
OSI LAYER DIAGRAM
| 7. Application |
|
| 6. Presentation |
|
| 5. Session |
|
| 4. Transport |
|
| 3. Network |
|
| 2. Data Link |
|
| 1. Physical |
|
- The TCP / IP Model : It consists of only four layers Application, Transport, Internet and Network LayerPhysical Layer: Ensures a safe and efficient transmission of data; consists of electronic circuits for data transmission.
- Data Link Layer: In charge of data encapsulation under the form of frame and their interpretation at the physical Layer.
- Network Layer: In charge of packets transmission from a source A to a destination B.
- Transport Layer: In charge of delivery of packets from a source process A to a destination process B
- Session layer: In charge of the management of dialogue between source and destination.
- Presentation Layer: Determines the format of the data transmitted to application, data compressing / decompressing ,encryption etc
- Application Layer:It contains the application which are used by a end- user, such as MicroSoft-Power Point, MicroSoft-Word etc.
TCP/IP Model :
| Application |
| Transport |
| Internet |
| Network Interface |
- Network Interface Layer: Provide the same functionality as the physical layer , data link layer and network layers in the OSI model and mapping between IP addresses and network physical addresses, Encapsulation of IP datagram, e.g. packets, in formats understandable by the network.
- Internet Layer: Based on the Internet Protocol(IP), which provides the frame for transmitting data from place A to place B.
- Transport Layer: Based on two main protocols: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol ) and UDP ( User Datagram Protocol )
- Application Layer: Combines the function of OSI application , presentation , and session layers, And Protocols involve in this layer : HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS etc.
Bandwidth : The number of bits that can be transmitted over a network in a given time, usually measured Hz(Hertz).
Broadband : Broadband is a term referred to some technologies that offers high speed internet connectivity depending on framework and environment. It is network connection with high enough bandwidth to allow for streaming audio and video. Broadband basically works through its bandwidth. As you increase the width of the band, so you get the speedy access to the internet.
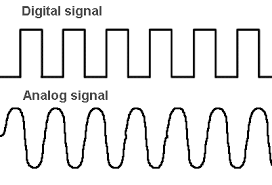
Analog and Digital Transmission:
- Analog Signal: An analog signal is one that is continous with respect to time and may take on any value within a given range of values. Human voice, video and music when converted to electric signalusing suitable devices produce analog signals. Its is denoted by sine waves. Landline phone uses analog signal.
- Digital signal: Digital signals are discrete time signals generated by digital modulation. It is denoted by square waves. Computers, CDs, DVDs, and other digital electronic devices uses digital signal.
Thank you and All the best!!
For always keep in touch with updates you can join or visit at Facebook Page or Twitter
