Introduction to Blockchain Technology PDF – Meaning, Types , Advantages
Blockchain Overview
Blockchain is the technology used in Bitcoin. It is a public distributed database holding encrypted ledgers.
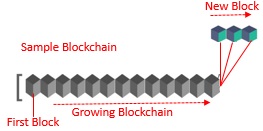
A block is the “current” part of a blockchain which records some or all of the recent transactions, and once completed goes into the blockchain as permanent database. Each time a block gets completed, a new block is generated.
How does Blockchain Technology work?
-> Blockchain Technology is a network of computers that all have same history of transactions.
-> Transactions recorded as blocks on network held by multiple people at the same time.
-> Every ten minutes of transactions become one block.
-> Database is not centralised i.e. it is distributed.
-> Each transactions validated by each of the individuals on the network.
-> Information in the block can’t be altered creating a clear history of each transaction.
-> First work on chain of blocks in 1991 by Stuart Haber & Scott Stornetta.
-> Bayer, Haber, Stornetta improve efficiency of technology in 1992.
-> First block chain conceptualised by person or group of people named Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008.
-> 2016 : Russia announces pilot project based on technology for automated voting system.
Block Chain Technology – Frequently Asked Questions
= Where did the digital transaction take place?
= How did the transaction take place?
= Who made the transaction?
= Was the transaction valid or not?
= How secure is the transaction?
= What is the legal validity of entities involved in transaction?
How Bitcoin solve issues with centralised banks?
Bitcoin solved the issues we had with centralised banks.
1. Bitcoin Blockchain has a distributed ledger.
2. The ledger is public for all to access.
3. Transactions are immutable, thus cannot be hacked.
4. Double spending is not allowed because of the basic structure of block transactions.
Blockchain Flowchart
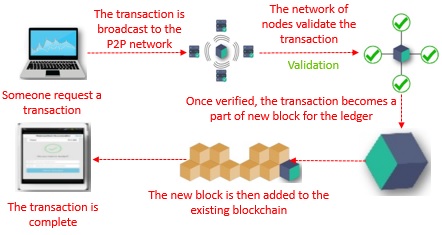
Blockchain Advantages – Use & Possibilities
-> Confidential communication cryptocurrency.
-> Safe, cost effective and fast bank transactions.
-> Secure legal documents, health data, notaries and personal documents.
-> Distribution of land records, government financial assistance.
-> Cloud storage, digital identification, smart communication & digital voting.
-> Property dealer use in their business.
-> Used in cloud hosting platform.
-> Universities use it as educational information.
-> Provides transparent platform to students, teachers and companies.
-> Financial companies use Blockchain for safety.
-> FinTech companies use platform for speed.
-> Makes it easy to get insurance loans.
Blockchain Disadvantages
For instance, when it comes to personal information that is available publicly, use of blockchain is not advised.
Types of Blockchain
1. Public Blockchain : Public blockchains have ledgers visible to everyone on the internet and anyone can verify and add a block of transactions to the block chain.
2. Private Blockchain : Private blockchains allow only specific people in the organization to verify and add transaction blocks but everyone on the internet is generally allowed to view.
3. Consortium Blockchain : Here, only a group of organisations (such as banks) can verify and add transactions but the ledger can open or restricted to select groups.
Blockchain in a Nutshell
The use of Mathematics to create a secure distributed ledger which enables transactions without the need for third parties.
Blockchain Features
Fraud Resistance i.e. Fraud Proof
Consistency i.e. Bockchain does not have accounts where hackers can modify the balance.
Maintenance Incentives i.e. Rather, it is the entire blockchain with transactions which make the system.
Example : Ethereum is an open-source, public, blockchain-based distributed computing platform.
Blockchain Use Cases
- Banking : Blockchain could cut up to $20 billion in middle-man costs per year. Hacking into banking ledgers becomes close to impossible. Solves the double spending problem. Reduces bank crises by a large extent.
- Payment & Transfer : Blockchain transfers are the highest in terms of security. Currently, Bitcoin runs on no fixed transaction fees. No bank account required. Anonymity is maintained.
- Healthcare
- Law Enforcement
- Voting : Election require authentication of voters identity, secure records keeping and trusted tallies. Blockchains are the medium for casting, tracking and counting votes without voter-fraud, lost records or fowl-play. Increases voter turnout.
- Online Music
- Real Estate
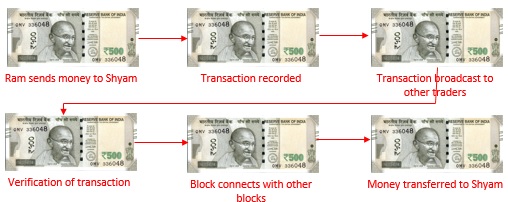
Cyber Laws In India
-> IT Act 2000 provide legal recognition for transactions carried out through electronic data. Act made amendment to IPC, 1860.
-> The Indian Evidence Act, 1872
-> The Banker’s Books Evidence Act, 1891
-> The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
-> IT Act, 2000 amended in 2008.
-> Provided additional focus on information security.
-> Added new sections on cyber terrorism, data protection.
-> Offences on creating false electronic record brought under section 463 of the IPC.
-> Cyber fraud, cheating brought under section 420.
Modes of Digital Transactions
-> Net Banking
-> Debit or Credit Card
-> Mobile apps
-> Mobile wallets
-> Electronic Clearing Services (ECS)
-> National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT)
-> Immediate Payment Service (IFS)
Advantages of Digital Transactions
1. Time saving, cost effective
2. Convenience
3. Reduces error
4. Less flow of cash
5. Tax-compliance
6. Removal of Black Economy
All the best for your upcoming exam!
You can join or visit at Facebook Page or Twitter for always keep in touch with further updates.
Read more articles….
