Periodic Table of Elements with Atomic Mass and Valency PDF Download – Classification of Elements
Periodic Table
- It is a tabular display of the chemical elements, organised on the basis of their properties.
- It contains horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns called group.
- Father of periodic table is Mendeleev.
Classification of Elements
The arrangement of the known elements in certain groups in such a way so that the elements with similar properties are grouped together is known as classification of elements.
Genesis of periodic classification
Origin and mode of formation of Periodic table are given below with details.
Lavoisier
- Classified the elements into metals and non-metals.
Dobereiner’s Triads
In 1829, Dobereiner, a German chemist arranged certain elements with similar properties in groups of three in such a way that the atomic mass of the middle element was nearly the same as the average atomic masses of the first and third elements.
| Tried | Atomic mass |
| Lithium | 7 |
| Sodium | 23 |
| Potassium | 39 |
Atomic mass of sodium = (39+7)/2 = 23
But only few elements could be covered under triads.
Newland’s law of octaves
In 1866, John’s Newlands, An English Chemist proposed the law of octaves by stating that, When elements are arranged in order to increasing atomic masses, every eighth elements has properties similar to the first, just like musical notes.
But this generalization was also rejected because it could not be extended to the elements with atomic mass more than 40.
Lother’s Mayer’s atomic volume curve
In 1869, Lother mayer plotted a graph between atomic volume of the elements and their atomic mass and he pointed that the elements with similar properties occupy similar position in the curve.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Law
- It is based upon the Mendeleev’s periodic law, which states “the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses.”
- It contains 7 periods and 8 groups, but 0 group is absent in this table.
- It contains gaps (free space) for the elements, not known at that time. e.g., Eka-boron, Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon, the properties of which had been found similar to the scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later.
- It have no fixed position for hydrogen, no space for isotopes, and not a regular arrangement of atomic masses.
Modern Periodic Table
- It was given by Moseley.
- It is based on modern periodic law, according to which “physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers.”
- It shows periodicity of properties.
- It contains 18 groups. First group, elements are called alkali metals, second group elements are called alkaline earth metals, 15 group elements are called pnicogens, elements of 16, 17 and 18 groups are called chalcogens, halogens and noble gases respectively.
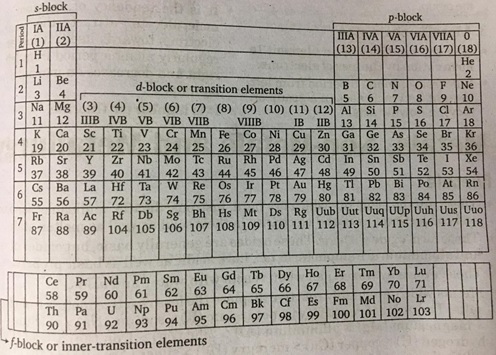
Long form of Periodic Table
- It is just graphical representation of aufbau principle. It is based on the electronic configuration of elements and contains 118 elements.
- It is divided into four blocks.
s-block
- This block elements are known as Alkali & Alkaline earth metals.
- It contains 1 and 2 group, i.e., hydrogen and alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Cs, Fr) and alkaline earth metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra).
- General electronic configuration of these elements is n s0-2.
- These elements are soft metals, electropositive and form basic oxides.
p-block
- These elements are known as Chalcogen, Picogens, Halogens and inerts gases.
- It comprises the last six groups (13-18).
- General electronic configuration of this block elements is n s2 np1-6
- It is the only block which contains metals, non-metal and metalloids.
- Heavier elements show inert pair effect.
- s and p-block elements are collectively called representative elements.
- Hg, Zn, Cu, Sc etc., are d-block elements but not the transition elements.
d-block
- These elements are also known as Transition elements.
- It comprises 10 groups (3 to 12).
- General electronic configuration of this block elements id (n – 1) r2 p6 , nd 1-10-12 nr.
- Elements of this block contain unpaired electrons and are paramagnetic.
- These elements show variable valency due to less difference in the energy of outer and penultimate shell.
- These elements are generally coloured, and used as catalyst.
f-block
- These elements are known as Inner transition elements.
- It usually offset below the rest of the Periodic Table, comprises of two rows. First row of 14 elements from atomic number 58 to 71 and is called Lanthanides series. The second row also contains 14 elements from atomic number 90 to 103 and is called Actinide series.
- General electronic configuration of this block elements is (n – 2)1 – 14 (n – 1) r2 p6 d0-12 nr.
- There are two series in this block 4f and 5f series. 4f series elements are called lanthanides and 5f series elements are called actinides.
- Elements of this block are called inner-transition elements and present in HIB(3) group only.
Periodic properties of Elements
Periodic properties are those which show a regular trend along a period and a group.
Atomic Size
- It generally increases on moving down the group because number of shells increases.
- It decreases along a period from left to right. Thus, size of alkali metal is largest and that of halogens is smallest in a period.
Note : Smallest atom is hydrogen and largest atom is cesium. Most poisonous metal is plutonium.
Valency
- It is the combining capacity of an element.
- It increases from 1 to 7 along a period with respect to hydrogen whereas with respect to oxygen, it first increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0.
- It remains the same in a group.
Note : Reactivity of metals increases while that of non-metals decreases on moving down the group.
Metallic character
- It is the tendency of an element to form cation by the loss of electrons.
- It decreases along a period from left to right and increases in a group on moving downwards.
Note : Metal with lowest density is lithium. Tungsten is the metal having highest melting point.
Atomic radii
The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons called atomic radius. It is not possible to measure the absolute value of atomic radius of an element. However, it may be expressed in three different forms covalent radii, metallic radii, Van der wall radii. The size of these atomic radii are as
Van der wall radii > metallic radii > covalent radii
Atomic radii decreases from left to right in a period and increases in a group from top to bottom.
Ionic radii
The effective distance from the centre of nucleus of the ion upto which it exerts its influence on the electron cloud is called ionic radii. The size of ionic radii and atomic radius are as
Anionic radii > Atomic radii > Cationic radii
Ionic radii decreases from left to right in a period and increases in a group from top to bottom.
Ionization Potential (I.P) or Energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from isolated gaseous atom is called Ionization Potential (I.P.) or Ionization Energy (I.E.)
A (g) – e + Energy required (I.P.) → A+ (g)
Ionization potential increases from left to right in a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group. However ionisation energy of Be, Mg, Ca, Sr is larger than ionization energy of B, Al, In, Tl respectively. Morever, ionisation energy of N, P is larger than ionisation energy of O, S, Se respecively. The unit of ionization energy is KJ/mol or eV/atom.
Electronic Affinity (Ea)
The energy released during addition of an extra electron in isolated gaseous atom is called electron Affinity.
A (g) + e → A– (g) + Energy released
It increases across a period from left to right, but EA of II(2), 15 group and 0 group is 0 or positive.
It decreases on moving down a group. It is highest for chlorine (Cl). The unit of electron affinity is KJ/mol or eV/atom.
Electronegativity (En)
The relative electron attracting tendency of an atom for a shared pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called electronegativity. It has no unit. Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative atom.
En = (IP + Ea)/ 5.6
Where En = Electronegtive, I.P. =Ionisation Energy, Ea = Electron Affinity.
- For ionic compound En value is greater than 1.7.
- For polar co-valent compound En value is less than 1.7.
- For non polar co-valent compound , En value is 0.
Electronegativity increases from left to right in a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group.
Lattice Energy
The amount of energy released during formation of one mole of ionic compound from its constituent ions is called Lattice energy.
Hydration Energy
The amount of energy released during dissolution of one mole of compound into water, is called hydration energy.
If hydration energy is greater than Lattice energy, then compound is soluble in water and if hydration energy is less than lattice energy, then compound is called insoluble in water.
Periodic Table PDF Download
Candidates can download the Periodic table PDF by clicking on below link.
Practice make a man perfect. All the best for your upcoming exam!
You can join or visit at ![]() or
or ![]() or
or ![]() for always keep in touch with further updates.
for always keep in touch with further updates.
