Election Commission of India Facts & Figure to Know | Points | Notes
- India’s first Chief Election Commissioner was Sukumar Sen.
- India’s first General Election was held between 1951 – 1952 in which 17.3 crore voters were registered.
- Article 326 (also know as Universal Adult Franchise) is also called as Right to vote and it is constitutional right but not fundamental right.
- Article 326 up to 1988 stated that minimum age to vote is 21 years.
- In 1988, 61st amendment act was brought in which voting age is reduced from 21 years to 18 years.
- Our current 25th Chief Election Commissioner is Rajiv Kumar and other Election Commissioner is Anup Chandra Pandey.
- In 17th General Election, there is 90 crore registered voters.
- There are 3 types of election [a. Lok Sabha Election/General Election, b. Rajya Sabha Election, c. Legislative Council Election/ State Assemble Election].
- We have 3 organs of Government [a. Legislative, b. Executive, c. Judiciary]
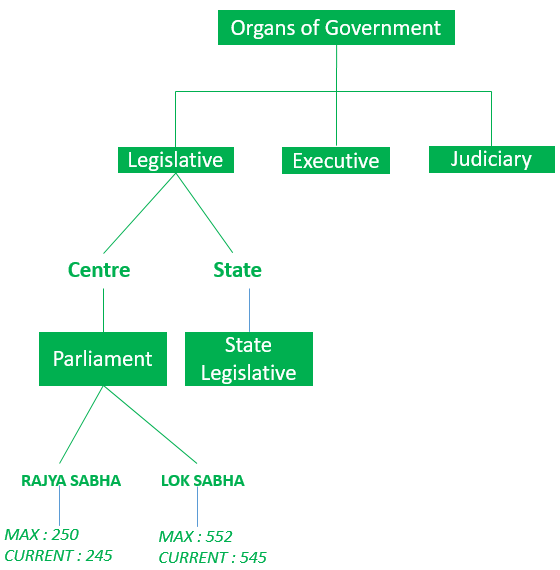
10. Rajya Sabha Seat Allocation – [233 State Assembly, 12 members are nominated directly by president]
11. Lok Sabha Seat Allocation – [530 members from State, 20 members from Union Territory, 2 Anglo Indians are appointed by President].
12. In Lok Sabha, party which gets more than 50% seat (i.e. gets 272 seats or more) formed the government in India. And that party leader will be appointed as Prime Minister.
13. In India Constitution Part XV, Election are covered in article 324 to 329.
14. Article 324 state that we will have an independent election commission in India which will conduct free and fair election. EC will conduct the elections for Parliament, State Assembly, President and Vice President.
15. Panchayat and Municipality were introduced through 73rd – 74th amendments in India. Municipality, Jila Prishad, Gram Panchayat, Panchayat Samiti and other local authorities election does not conducted by ECI but conducted by State Election Commission.

16. CEC, 2 ECs are appointed by President. All 3 have equal power. And dispute are solved through majority. Salary basic allowances, etc are similar to that of a Supreme Court Judge.
17. Election in district are supervised by District Election Officer.
18. Election in State/UT are supervised by Chief Electoral Officer.
19. Election in Parliament are supervised by Returning Officer.
20. India used paper ballots till the 1990s.
21. Electoral voting machines (EVMs) were tried for the first time on an experiment basis for the 1982 Kerala State Legislative Assembly Elections.
22. Prior to the introduction of electronic voting, India used paper ballots and manual counting. This Voter-verified paper audit trail (VVPAT) system was first used with EVMs in a by-poll in Sep 2013 in Noksen (Assembly Constituency) in Nagaland and eventually in all elections from Sep 2013 onwards in various Legislative elections in the country.
23. In 2014, none of the above(NOTA) was also added as an option on the voting machines which is now a mandatory option to be provided in any election.
24. Ink which is applied during voting is called as Indelible Ink. This ink is manufactured by Mysure Paint & Varnish Limited and supply in more than 20 countries.
All the best for your upcoming exam!
You can join or visit at Facebook Page or Twitter for always keep in touch with further updates.
Read more articles….
